Animasi Sinar-X Buatan Tersuai
Oleh Infomedikini
Pada 15 March 2024
Justeru bagi meningkatkan kefahaman terhadap subjek yang tersedia kompleks ini maka saya terpanggil untuk menghasilkan animasi sinar-X komprehensif.
Sinar-X
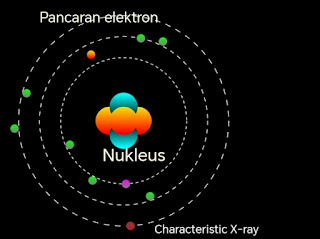
Apabila elektron dipecut ke arah atom seperti tungsten (imej-1) maka akan berlaku interaksi antara elektron yang dipancarkan dengan atom tungsten.

Imej 1
Hasil daripada interaksi tersebut adalah gelombang elektromagnet yang dikenali sebagai sinar-X. Terdapat 2 jenis sinar-X
-
Bremsstrahlung X-ray
Characteristic X-ray
Bremsstrahlung X-ray
"Terbentuk bila pecutan elektron mendekati nukleus atom lalu elektron tersebut melencong dari laluan asal dan menjadi perlahan".
Adapun tenaga elektron yang berkurangan tidak hilang sebaliknya ditukar kepada tenaga foton iaitu lebih dikenali sebagai sinar-X. Video 1
Video 1: Bremsstrahlung X-ray
Characteristic X-ray
"Terbentuk bila elektron berkelajuan tinggi yang mempunyai tenaga lebih tinggi daripada tenaga ikatan elektron atom melanggar keluar elektron daripada orbit."
Perpindahan elektron dari orbit sebelah luar (paras tenaga tinggi) ke orbit sebelah dalam (paras tenaga rendah) akan diikuti dengan pembebasan tenaga dalam bentuk sinar-X (X-ray). Video 2.
Video 2: Characteristic X-ray
Penghargaan: Terima kasih buat Hazlinda atas nasihat dan pembetulan yang diajukan.
Last-Modified: Teu, 14 Mei 2024 22:09:56 GMT
Home










Ulasan